
NeoMesh Protocol
NeoMesh is a wireless mesh protocol designed for IoT networks of any size. Be it small, massive or even dense.
Wireless Mesh
Networking Reimagined
NeoMesh is a wireless mesh protocol designed for small, medium and massive-scale IoT networks — combining ultra-low power operation, automatic self-organization, and robust data delivery across thousands of battery-powered devices.
Where traditional mesh networks rely on fixed roles (routers, end-devices, coordinators), NeoMesh is flat and fully decentralized. All devices have the same role: they generate, receive, and intelligently route data. This makes deployment simpler, power consumption lower, and scalability virtually unlimited.
View products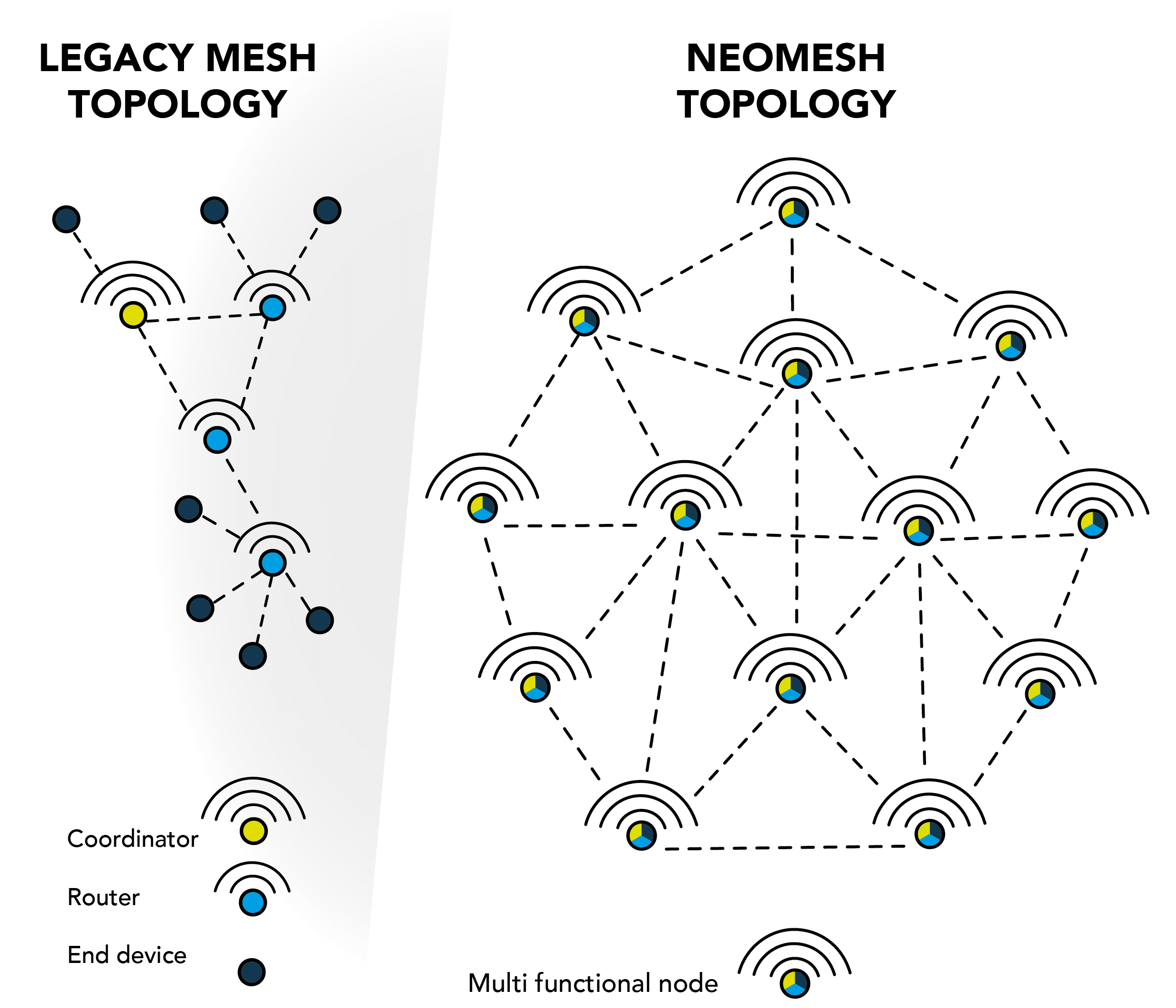
A Smarter Way to Mesh
The architecture eliminates planning and power constraints that limit legacy protocols like IEEE 802.15.4, where router nodes must remain awake and mains powered, and leaf nodes are limited to nearby connections. Instead, NeoMesh nodes collaborate, building up a dynamic, self-healing mesh. Each node maintains a list of selected neighbours — based not only on physical proximity, but also link quality and network dynamics. These relationships adapt in real time, ensuring optimal performance as nodes move, join, or leave the network. Because all nodes are battery-powered and self-routing, you can install devices exactly where they’re needed — no need to worry about mains power, routers, or coverage gaps. Just add nodes, and the network expands automatically.
NeoMesh supports both 2.4 GHz and sub-GHz ISM bands, and is available with FSK or LoRa modulation, giving you flexibility in radio range and deployment environments.
FSK or LoRa® – Choosing the right PHY layer for NeoMesh
The PHY layer, or Physical Layer, is the foundation of any wireless communication system. It defines how data is physically transmitted over the air — including the modulation scheme, frequency, data rate, and signal encoding. The choice of PHY has a direct impact on range, reliability, power consumption, and overall network performance. In NeoMesh, the PHY layer determines how well the network can adapt to different environments — from dense indoor buildings to remote agricultural fields — whether using traditional FSK or long-range LoRa modulation.
FSK Modulation
FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) is NeoMesh’s standard modulation option. It offers high data rates, efficient use of spectrum, and lower latency. Perfect for applications where data must be moved quickly and reliably over shorter to medium distances (e.g. indoor monitoring, building automation, wireless sensor networks). Because FSK modulation requires less overhead in coding and spread techniques, it tends to be more packet‑efficient and simpler in receiver design. It will normally enable the lowest average current consumption as the Time on Air is shorter due to the higher bitrate.
LoRa® Modulation
For deployments needing extended range, superior sensitivity, enhanced noise resilience or better performance in non‑line‑of‑sight (NLOS) environments, NeoMesh on LoRa® modulation is designed to meet those needs. LoRa® modulation trades off raw data throughput for enhanced sensitivity, stronger tolerance to interference, and long battery life under challenging link conditions. Ideal for remote sensors in agriculture, field monitoring, or dispersed outdoor networks.
No matter what PHY layer, ie. modulation type and frequency band you use, the NeoMesh protocol provides the same overall functionality and key benefits of being highly Reliable, ultra scalable and truly low power for all devices in the wireless mesh network.
Truly Low Power – For Every Node in the Network
NeoMesh is built for true ultra-low power operation, allowing each node in the network to run on a small battery for years — not just the end devices.
Unlike traditional mesh networks that rely on always-on routers (which requires mains power), NeoMesh has no dedicated routers. All nodes are equal: they send and receive their own data and also forward data for others — all while staying in low-power sleep mode the majority of the time.
How it works
NeoMesh uses precise time synchronization across the network. This ensures all nodes wake up at just the right moment to either transmit or receive. Outside these scheduled moments, radios remain asleep, dramatically reducing power consumption.
This mechanism is called Scheduled Data (SCD). Each node periodically transmits a data packet — whether or not it has payload data to send. This keeps neighboring relationships alive, maintains routes, and ensures the mesh stays intact even in dynamic environments.
Power vs. Latency
Shorter SCD intervals (e.g. 1–5 seconds)
• More frequent communication
• Higher throughput
• Lower latency (a few seconds in small networks)
• More power consumption
Longer SCD intervals (e.g. 15–30 seconds)
• Less frequent communication
• Lower throughput
• Higher latency (up to a few minutes in large networks)
• Much lower power consumption – as low as 15 µA average
Even with the higher communication rate, all nodes still remain low power thanks to the strict scheduling. And since NeoMesh includes high-accuracy timestamps in each packet, your application always knows exactly when the data was created, regardless of delivery delay.
Built to Scale – Effortlessly
NeoMesh is designed to scale — not just to dozens or hundreds of devices, but to thousands. We’ve successfully demonstrated networks with over 1000 devices operating seamlessly in a single NeoMesh network. Every Device is a Router — Without the Power Drain. In NeoMesh, every node is a full participant in the mesh. This is possible thanks to NeoMesh’s time-synchronized architecture, which ensures that even as nodes forward data across many hops, they only wake up at scheduled intervals — keeping power consumption to a minimum. Unlike traditional mesh protocols that rely on mains-powered routers, NeoMesh has no dedicated infrastructure. There are no always-on nodes, there is no hierarchy, and no centralized controller. The entire network is fully distributed and self-governing.
Sends and receives data
Each node sends and receives its own data
Routes data intelligently
Each node routes data efficiently in conjunction with other nodes
Ultra-low power
Power consumption is always ultra low
Truly Massive Networks
Our standard modules support up to 65,000 nodes in a single network. On platforms with more memory, that number can be even higher.
NeoMesh uses a patented Speed Routing algorithm, where each node dynamically determines the next-best-hop based on real-time link conditions — rather than using fixed paths or global routing tables. This ensures the network remains efficient and responsive, no matter how large it gets.
Flexible and Resilient Deployment
• You can install nodes anywhere — no need for routers or repeaters
• Add extra nodes to bridge gaps or extend coverage — the network will automatically adapt
• Place gateways wherever it makes sense — at the edge, in the center, or distributed
• Add or remove nodes at any time — the network topology reconfigures automatically
Even mobile nodes are supported. As they move, they detect and synchronize with new neighbors, maintaining their role in the mesh, as fully functional, low-power routers.
Designed for flexibility and scale
• Dynamic environments
• Retrofit of smart solutions in buildings or elsewhere
• Long-term; future proof
No infrastructure. No planning overhead. Just scalable wireless networking — the NeoMesh way.
Reliable and Secure by Design
In NeoMesh, every packet takes the best possible path through the network — and that path can change every time. Routes are determined dynamically using our patented Speed Routing algorithm, which always selects the next-best-hop based on current radio conditions. This means no fixed routing tables, no single points of failure and better reliability in larger, denser networks. Data packets between the same origin and destination will often take different routes, adding natural redundancy. If one path is temporarily blocked or degraded, another will take its place — automatically.
Built-In Redundancy and Robustness
NeoMesh networks are self-healing and highly resilient. Because every node is capable of routing, and because there’s no dependency on specific infrastructure nodes, the network will keep functioning even if some devices are removed, powered off, or damaged.
To further improve reliability, NeoMesh uses channel hopping. Each communication event takes place on a different radio channel, cycling through a predefined set. This minimizes interference and avoids issues like fading or blocking, which often occur in fixed-frequency systems — especially in congested environments.
Dual-Layer Acknowledgements
Local ACK:
Every hop between source and destination includes a local handshake. A packet is only removed from the sender’s queue once the next node confirms successful receipt. This provides hop-by-hop delivery assurance.
Global ACK:
For critical data, a full acknowledgment can be routed from the destination back to the origin. This ensures end-to-end confirmation where needed — though in most cases, the local ACK system alone is sufficient.
To ensure data integrity, NeoMesh uses a CRC32-equivalent error check, providing robust protection against corrupted transmissions.
Encrypted from the Ground Up
All communication in NeoMesh is encrypted using the AES128 symmetric block cipher, including both data payloads and internal network traffic. A challenge/response mechanism ensures that even identical payloads appear entirely different over the air — making playback attacks virtually impossible.
Monitoring Network Health
The NeoMesh gateway software includes an optional monitoring tool that provides real-time insight into network status. If a node drops offline — whether it sends data frequently or only occasionally — the system will detect it and can trigger alerts automatically.
Choose the Right Frequency Band
NeoMesh supports both 2.4 GHz and sub-GHz frequency bands:
• 2.4 GHz is globally available, but often crowded
• Sub-GHz (868 MHz / 915 MHz) offers longer range, better penetration, and lower interference
NeoMesh is also available with LoRa modulation, providing even greater sensitivity and range — at both 2.4 GHz and sub-GHz.
